datetime:2023/09/18 10:18
author:nzb
该项目来源于大佬的动手学ROS2
5.动作之CPP实现
上一节介绍了Action通信并一起自定义了一个接口,本节我们尝试使用接口来利用动作通信控制机器人。
1.创建功能包和节点
1.1 创建功能包
创建example_action_rclcpp功能包,添加robot_control_interfaces、rclcpp_action、rclcpp三个依赖,自动创建action_robot_01
节点,并手动创建action_control_01.cpp节点。
cd chapt4_ws/
ros2 pkg create example_action_rclcpp --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp rclcpp_action robot_control_interfaces --destination-directory src --node-name action_robot_01 --maintainer-name "fishros" --maintainer-email "fishros@foxmail.com"
touch src/example_action_rclcpp/src/action_control_01.cpp
接着我们创建Robot类的头文件和CPP文件。
touch src/example_action_rclcpp/include/example_action_rclcpp/robot.h
touch src/example_action_rclcpp/src/robot.cpp
创建完成后目录结构
.
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── include
│ └── example_action_rclcpp
│ └── robot.h
├── package.xml
└── src
├── action_control_01.cpp
├── action_robot_01.cpp
└── robot.cpp
3 directories, 6 files
1.2 robot.h
/*
copyright
*/
#ifndef EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
#define EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "robot_control_interfaces/action/move_robot.hpp"
class Robot {
public:
Robot() = default;
~Robot() = default;
private:
};
#endif // EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
1.3 robot.cpp
暂时为空,第二部分编写
#include "example_action_rclcpp/robot.h"
1.4 action_robot_01.cpp
#include "example_action_rclcpp/robot.h"
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "robot_control_interfaces/action/move_robot.hpp"
// 创建一个ActionServer类
class ActionRobot01 : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
explicit ActionRobot01(std::string name) : Node(name) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "节点已启动:%s.", name.c_str());
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
auto action_server = std::make_shared<ActionRobot01>("action_robot_01");
rclcpp::spin(action_server);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
1.5 action_control_01.cpp
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "robot_control_interfaces/action/move_robot.hpp"
class ActionControl01 : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
explicit ActionControl01(std::string name): Node(name) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "节点已启动:%s.", name.c_str());
}
}; // class ActionControl01
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
auto action_client = std::make_shared<ActionControl01>("action_robot_cpp");
rclcpp::spin(action_client);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
1.6 CMakeList.txt
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(robot_control_interfaces REQUIRED)
find_package(example_interfaces REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp_action REQUIRED)
# action_robot节点
add_executable(action_robot_01
src/robot.cpp
src/action_robot_01.cpp
)
target_include_directories(action_robot_01 PUBLIC
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include>)
target_compile_features(action_robot_01 PUBLIC c_std_99 cxx_std_17) # Require C99 and C++17
ament_target_dependencies(
action_robot_01
"rclcpp"
"rclcpp_action"
"robot_control_interfaces"
"example_interfaces"
)
install(TARGETS action_robot_01
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})
# action_control节点
add_executable(action_control_01
src/action_control_01.cpp
)
target_include_directories(action_control_01 PUBLIC
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include>)
target_compile_features(action_control_01 PUBLIC c_std_99 cxx_std_17) # Require C99 and C++17
ament_target_dependencies(
action_control_01
"rclcpp"
"rclcpp_action"
"robot_control_interfaces"
"example_interfaces"
)
install(TARGETS action_control_01
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})
2.编写机器人类
机器人类主要负责移动机器人和提供当前机器人的状态,我们设计几个函数来实现该功能。
2.1 robot.h
#ifndef EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
#define EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "robot_control_interfaces/action/move_robot.hpp"
class Robot {
public:
using MoveRobot = robot_control_interfaces::action::MoveRobot;
Robot() = default;
~Robot() = default;
float move_step(); /*移动一小步,请间隔500ms调用一次*/
bool set_goal(float distance); /*移动一段距离*/
float get_current_pose();
int get_status();
bool close_goal(); /*是否接近目标*/
void stop_move(); /*停止移动*/
private:
float current_pose_ = 0.0; /*声明当前位置*/
float target_pose_ = 0.0; /*目标距离*/
float move_distance_ = 0.0; /*目标距离*/
std::atomic<bool> cancel_flag_{false}; /*取消标志*/
int status_ = MoveRobot::Feedback::STATUS_STOP;
};
#endif // EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_
2.2 robot.cpp
#include "example_action_rclcpp/robot.h"
/*移动一小步,请间隔500ms调用一次*/
float Robot::move_step() {
int direct = move_distance_ / fabs(move_distance_);
float step = direct * fabs(target_pose_ - current_pose_) *
0.1; /* 每一步移动当前到目标距离的1/10*/
current_pose_ += step;
std::cout << "移动了:" << step << "当前位置:" << current_pose_ << std::endl;
return current_pose_;
}
/*移动一段距离*/
bool Robot::set_goal(float distance) {
move_distance_ = distance;
target_pose_ += move_distance_;
/* 当目标距离和当前距离大于0.01同意向目标移动 */
if (close_goal()) {
status_ = MoveRobot::Feedback::STATUS_STOP;
return false;
}
status_ = MoveRobot::Feedback::STATUS_MOVEING;
return true;
}
float Robot::get_current_pose() { return current_pose_; }
int Robot::get_status() { return status_; }
/*是否接近目标*/
bool Robot::close_goal() { return fabs(target_pose_ - current_pose_) < 0.01; }
void Robot::stop_move() {
status_ = MoveRobot::Feedback::STATUS_STOP;
} /*停止移动*/
3.编写机器人节点
class ActionRobot01 : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
using MoveRobot = robot_control_interfaces::action::MoveRobot;
using GoalHandleMoveRobot = rclcpp_action::ServerGoalHandle<MoveRobot>;
explicit ActionRobot01(std::string name) : Node(name) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "节点已启动:%s.", name.c_str());
using namespace std::placeholders; // NOLINT
this->action_server_ = rclcpp_action::create_server<MoveRobot>(
this, "move_robot",
std::bind(&ActionRobot01::handle_goal, this, _1, _2),
std::bind(&ActionRobot01::handle_cancel, this, _1),
std::bind(&ActionRobot01::handle_accepted, this, _1));
}
private:
Robot robot;
rclcpp_action::Server<MoveRobot>::SharedPtr action_server_;
rclcpp_action::GoalResponse handle_goal(
const rclcpp_action::GoalUUID& uuid,
std::shared_ptr<const MoveRobot::Goal> goal) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Received goal request with distance %f",
goal->distance);
(void)uuid;
if (fabs(goal->distance > 100)) {
RCLCPP_WARN(this->get_logger(), "目标距离太远了,本机器人表示拒绝!");
return rclcpp_action::GoalResponse::REJECT;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),
"目标距离%f我可以走到,本机器人接受,准备出发!",
goal->distance);
return rclcpp_action::GoalResponse::ACCEPT_AND_EXECUTE;
}
rclcpp_action::CancelResponse handle_cancel(
const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleMoveRobot> goal_handle) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Received request to cancel goal");
(void)goal_handle;
robot.stop_move(); /*认可取消执行,让机器人停下来*/
return rclcpp_action::CancelResponse::ACCEPT;
}
void execute_move(const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleMoveRobot> goal_handle) {
const auto goal = goal_handle->get_goal();
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "开始执行移动 %f 。。。", goal->distance);
auto result = std::make_shared<MoveRobot::Result>();
rclcpp::Rate rate = rclcpp::Rate(2);
robot.set_goal(goal->distance);
while (rclcpp::ok() && !robot.close_goal()) {
robot.move_step();
auto feedback = std::make_shared<MoveRobot::Feedback>();
feedback->pose = robot.get_current_pose();
feedback->status = robot.get_status();
goal_handle->publish_feedback(feedback);
/*检测任务是否被取消*/
if (goal_handle->is_canceling()) {
result->pose = robot.get_current_pose();
goal_handle->canceled(result);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Goal Canceled");
return;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Publish Feedback"); /*Publish feedback*/
rate.sleep();
}
result->pose = robot.get_current_pose();
goal_handle->succeed(result);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Goal Succeeded");
}
void handle_accepted(const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleMoveRobot> goal_handle) {
using std::placeholders::_1;
std::thread{std::bind(&ActionRobot01::execute_move, this, _1), goal_handle}
.detach();
}
};
代码解析
上面的代码信息量有些大,但都是围绕着Action展开的,带你一步步分解。
首先找到创建Action的API:https://docs.ros2.org/latest/api/rclcpp_action/
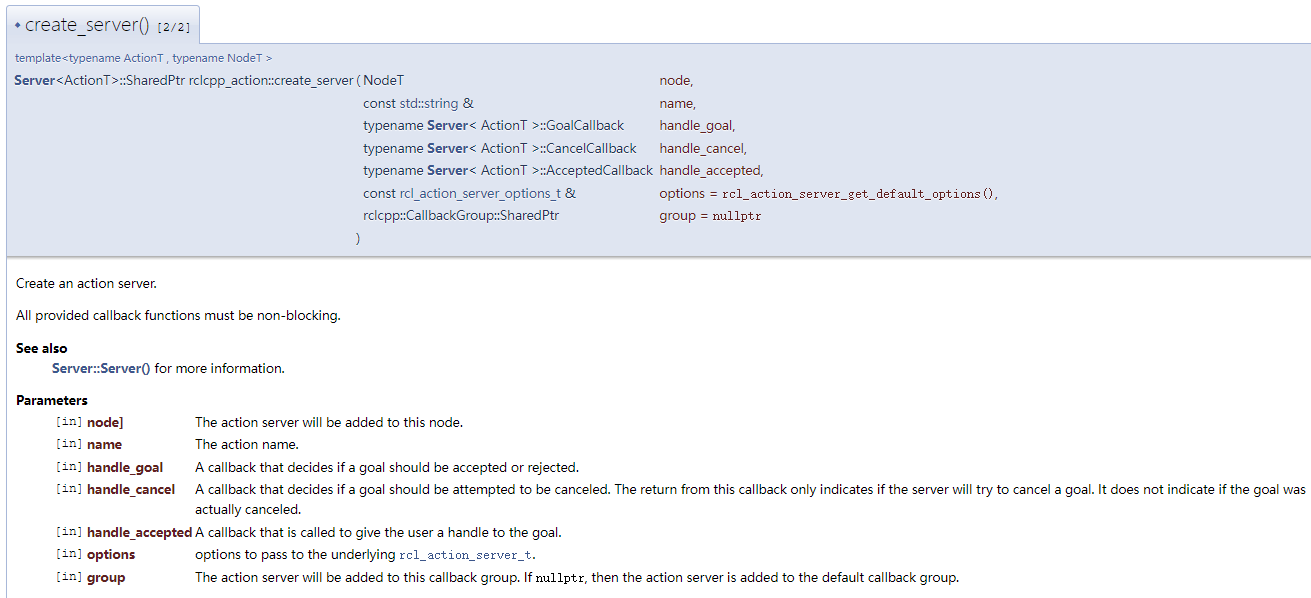
Action使用了三个回调函数,分别用于处理收到目标、收到停止、确认接受执行。
- handle_goal,收到目标,反馈是否可以执行该目标,可以则返回
ACCEPT_AND_EXECUTE,不可以则返回REJECT - handle_cancel,收到取消运行请求,可以则返回
ACCEPT,不可以返回REJECT。 - handle_accepted,处理接受请求,当handle_goal中对移动请求
ACCEPT后则进入到这里进行执行,这里我们是单独开了个线程进行执行execute_move函数,目的是避免阻塞主线程。
执行函数execute_move,调用机器人,进行一步步的移动,这里我们采用了while循环的形式,不断调用机器人移动并获取机器人的位置,通过feedback进行反馈。同时检测任务是否被取消,如顺利执行完成则反馈最终结果。
代码中我们还用到了Rate函数来精准控制循环的周期,让其保持为2HZ,关于Rate等流程控制的工具,放到进阶篇来讲解。
4.编写控制节点
先看API:rclcpp_action: rclcpp_action Namespace Reference (ros2.org)
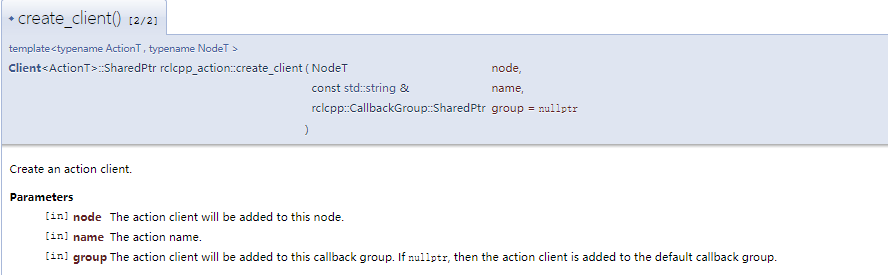
接着看代码
class ActionControl01 : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
using MoveRobot = robot_control_interfaces::action::MoveRobot;
using GoalHandleMoveRobot = rclcpp_action::ClientGoalHandle<MoveRobot>;
explicit ActionControl01(
std::string name,
const rclcpp::NodeOptions& node_options = rclcpp::NodeOptions())
: Node(name, node_options) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "节点已启动:%s.", name.c_str());
this->client_ptr_ =
rclcpp_action::create_client<MoveRobot>(this, "move_robot");
this->timer_ =
this->create_wall_timer(std::chrono::milliseconds(500),
std::bind(&ActionControl01::send_goal, this));
}
void send_goal() {
using namespace std::placeholders;
this->timer_->cancel();
if (!this->client_ptr_->wait_for_action_server(std::chrono::seconds(10))) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(),
"Action server not available after waiting");
rclcpp::shutdown();
return;
}
auto goal_msg = MoveRobot::Goal();
goal_msg.distance = 10;
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Sending goal");
auto send_goal_options =
rclcpp_action::Client<MoveRobot>::SendGoalOptions();
send_goal_options.goal_response_callback =
std::bind(&ActionControl01::goal_response_callback, this, _1);
send_goal_options.feedback_callback =
std::bind(&ActionControl01::feedback_callback, this, _1, _2);
send_goal_options.result_callback =
std::bind(&ActionControl01::result_callback, this, _1);
this->client_ptr_->async_send_goal(goal_msg, send_goal_options);
}
private:
rclcpp_action::Client<MoveRobot>::SharedPtr client_ptr_;
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
void goal_response_callback(GoalHandleMoveRobot::SharedPtr goal_handle) {
if (!goal_handle) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was rejected by server");
} else {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),
"Goal accepted by server, waiting for result");
}
}
void feedback_callback(
GoalHandleMoveRobot::SharedPtr,
const std::shared_ptr<const MoveRobot::Feedback> feedback) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Feedback current pose:%f", feedback->pose);
}
void result_callback(const GoalHandleMoveRobot::WrappedResult& result) {
switch (result.code) {
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::SUCCEEDED:
break;
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::ABORTED:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was aborted");
return;
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::CANCELED:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was canceled");
return;
default:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Unknown result code");
return;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Result received: %f", result.result->pose);
// rclcpp::shutdown();
}
}; // class ActionControl01
代码解析
创建客户端简单,发送请求的时候可以指定三个回调函数:
- goal_response_callback,目标的响应回调函数。
- feedback_callback,执行过程中进度反馈接收回调函数。
- result_callback,最终结果接收的回调函数。
这里利用了定时器完成了定时请求的功能,请求一次后就立马使用timer_->cancel();取消掉了这个定时器,如此就实现了节点启动后定时发一次请求的功能。
5.编译测试
一个终端,运行机器人节点
cd chapt4_ws/
colcon build --packages-up-to example_action_rclcpp
source install/setup.bash
ros2 run example_action_rclcpp action_robot_01
新终端,运行控制节点
source install/setup.bash
ros2 run example_action_rclcpp action_control_01
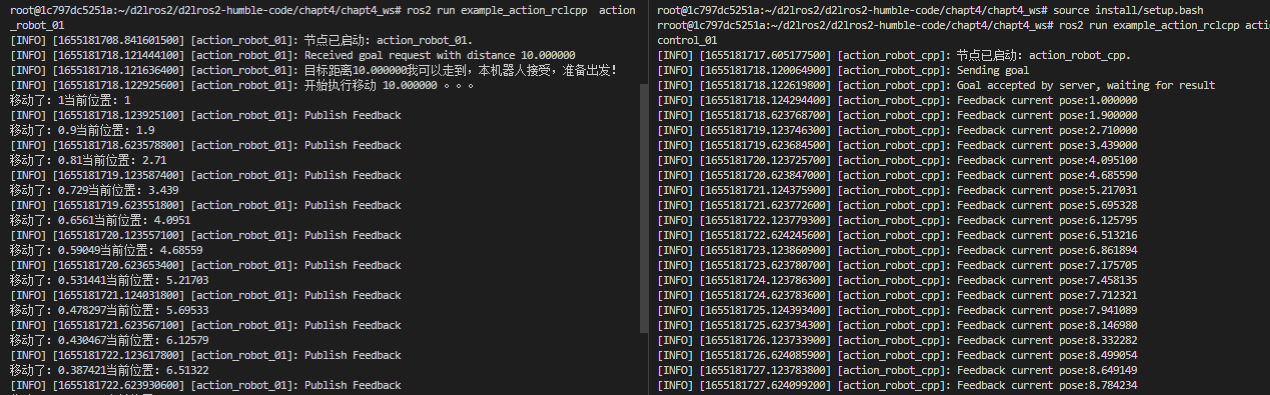
执行完成
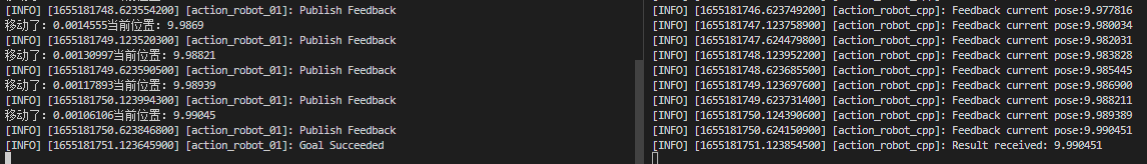
6.总结与测试
上面只做了简单的测试,你可以尝试再编写一个定时器,在节点启动的第5s时发送取消执行请求,看看是否可以让机器人停下来。
本节我们利用rclcpp_action的API实现了Action通信的测试,Action在后续的机器人开发中并没那么常用,但是其思想比较重要,应该掌握。