datetime:2022/02/05 16:58
author:nzb
Go语言动手写Web框架 - Gee第三天 前缀树路由Router
本文是 7天用Go从零实现Web框架Gee教程系列的第三篇。
- 使用 Trie 树实现动态路由(dynamic route)解析。
- 支持两种模式
:name和*filepath,代码约150行。
Trie 树简介
之前,我们用了一个非常简单的map结构存储了路由表,使用map存储键值对,索引非常高效,但是有一个弊端,键值对的存储的方式,只能用来索引静态路由。那如果我们想支持类似于/hello/:name这样的动态路由怎么办呢?所谓动态路由,即一条路由规则可以匹配某一类型而非某一条固定的路由。例如/hello/:name,可以匹配/hello/geektutu、hello/jack等。
动态路由有很多种实现方式,支持的规则、性能等有很大的差异。例如开源的路由实现gorouter支持在路由规则中嵌入正则表达式,例如/p/[0-9A-Za-z]+,即路径中的参数仅匹配数字和字母;另一个开源实现httprouter就不支持正则表达式。著名的Web开源框架gin 在早期的版本,并没有实现自己的路由,而是直接使用了httprouter,后来不知道什么原因,放弃了httprouter,自己实现了一个版本。
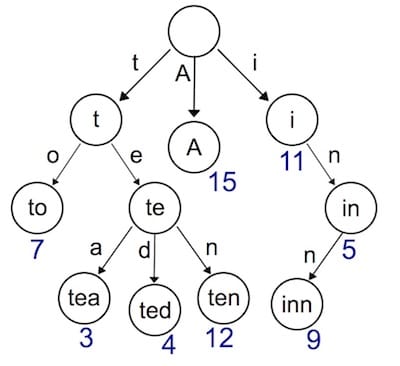
实现动态路由最常用的数据结构,被称为前缀树(Trie树)。看到名字你大概也能知道前缀树长啥样了:每一个节点的所有的子节点都拥有相同的前缀。这种结构非常适用于路由匹配,比如我们定义了如下路由规则:
- /:lang/doc
- /:lang/tutorial
- /:lang/intro
- /about
- /p/blog
- /p/related
我们用前缀树来表示,是这样的。
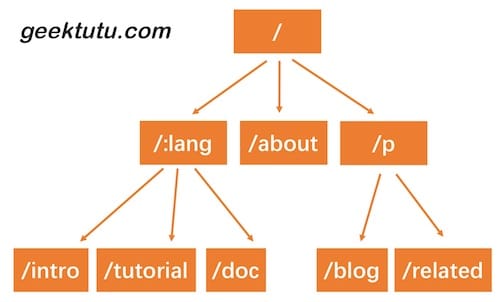
HTTP请求的路径恰好是由/分隔的多段构成的,因此,每一段可以作为前缀树的一个节点。我们通过树结构查询,如果中间某一层的节点都不满足条件,那么就说明没有匹配到的路由,查询结束。
接下来我们实现的动态路由具备以下两个功能。
- 参数匹配
:。例如/p/:lang/doc,可以匹配/p/c/doc和/p/go/doc。 - 通配
*。例如/static/*filepath,可以匹配/static/fav.ico,也可以匹配/static/js/jQuery.js,这种模式常用于静态服务器,能够递归地匹配子路径。
Trie 树实现
首先我们需要设计树节点上应该存储那些信息。
type node struct {
pattern string // 待匹配路由,例如 /p/:lang
part string // 路由中的一部分,例如 :lang
children []*node // 子节点,例如 [doc, tutorial, intro]
isWild bool // 是否精确匹配,part 含有 : 或 * 时为true
}
与普通的树不同,为了实现动态路由匹配,加上了isWild这个参数。即当我们匹配 /p/go/doc/这个路由时,第一层节点,p精准匹配到了p,第二层节点,go模糊匹配到:lang,那么将会把lang这个参数赋值为go,继续下一层匹配。我们将匹配的逻辑,包装为一个辅助函数。
// 第一个匹配成功的节点,用于插入
func (n *node) matchChild(part string) *node {
for _, child := range n.children {
if child.part == part || child.isWild {
return child
}
}
return nil
}
// 所有匹配成功的节点,用于查找
func (n *node) matchChildren(part string) []*node {
nodes := make([]*node, 0)
for _, child := range n.children {
if child.part == part || child.isWild {
nodes = append(nodes, child)
}
}
return nodes
}
对于路由来说,最重要的当然是注册与匹配了。开发服务时,注册路由规则,映射handler;访问时,匹配路由规则,查找到对应的handler。因此,Trie 树需要支持节点的插入与查询。插入功能很简单,递归查找每一层的节点,如果没有匹配到当前part的节点,则新建一个,有一点需要注意,/p/:lang/doc只有在第三层节点,即doc节点,pattern才会设置为/p/:lang/doc。p和:lang节点的pattern属性皆为空。因此,当匹配结束时,我们可以使用n.pattern == ""来判断路由规则是否匹配成功。例如,/p/python虽能成功匹配到:lang,但:lang的pattern值为空,因此匹配失败。查询功能,同样也是递归查询每一层的节点,退出规则是,匹配到了*,匹配失败,或者匹配到了第len(parts)层节点。
func (n *node) insert(pattern string, parts []string, height int) {
if len(parts) == height {
n.pattern = pattern
return
}
part := parts[height]
child := n.matchChild(part)
if child == nil {
child = &node{part: part, isWild: part[0] == ':' || part[0] == '*'}
n.children = append(n.children, child)
}
child.insert(pattern, parts, height+1)
}
func (n *node) search(parts []string, height int) *node {
if len(parts) == height || strings.HasPrefix(n.part, "*") {
if n.pattern == "" {
return nil
}
return n
}
part := parts[height]
children := n.matchChildren(part)
for _, child := range children {
result := child.search(parts, height+1)
if result != nil {
return result
}
}
return nil
}
Router
Trie 树的插入与查找都成功实现了,接下来我们将 Trie 树应用到路由中去吧。我们使用 roots 来存储每种请求方式的Trie 树根节点。使用 handlers 存储每种请求方式的 HandlerFunc 。getRoute 函数中,还解析了:和*两种匹配符的参数,返回一个 map 。例如/p/go/doc匹配到/p/:lang/doc,解析结果为:{lang: "go"},/static/css/geektutu.css匹配到/static/*filepath,解析结果为{filepath: "css/geektutu.css"}。
day3-router/gee/router.go
type router struct {
roots map[string]*node
handlers map[string]HandlerFunc
}
// roots key eg, roots['GET'] roots['POST']
// handlers key eg, handlers['GET-/p/:lang/doc'], handlers['POST-/p/book']
func newRouter() *router {
return &router{
roots: make(map[string]*node),
handlers: make(map[string]HandlerFunc),
}
}
// Only one * is allowed
func parsePattern(pattern string) []string {
vs := strings.Split(pattern, "/")
parts := make([]string, 0)
for _, item := range vs {
if item != "" {
parts = append(parts, item)
if item[0] == '*' {
break
}
}
}
return parts
}
func (r *router) addRoute(method string, pattern string, handler HandlerFunc) {
parts := parsePattern(pattern)
key := method + "-" + pattern
_, ok := r.roots[method]
if !ok {
r.roots[method] = &node{}
}
r.roots[method].insert(pattern, parts, 0)
r.handlers[key] = handler
}
func (r *router) getRoute(method string, path string) (*node, map[string]string) {
searchParts := parsePattern(path)
params := make(map[string]string)
root, ok := r.roots[method]
if !ok {
return nil, nil
}
n := root.search(searchParts, 0)
if n != nil {
parts := parsePattern(n.pattern)
for index, part := range parts {
if part[0] == ':' {
params[part[1:]] = searchParts[index]
}
if part[0] == '*' && len(part) > 1 {
params[part[1:]] = strings.Join(searchParts[index:], "/")
break
}
}
return n, params
}
return nil, nil
}
Context与handle的变化
在 HandlerFunc 中,希望能够访问到解析的参数,因此,需要对 Context 对象增加一个属性和方法,来提供对路由参数的访问。我们将解析后的参数存储到Params中,通过c.Param("lang")的方式获取到对应的值。
day3-router/gee/context.go
type Context struct {
// origin objects
Writer http.ResponseWriter
Req *http.Request
// request info
Path string
Method string
Params map[string]string
// response info
StatusCode int
}
func (c *Context) Param(key string) string {
value, _ := c.Params[key]
return value
}
day3-router/gee/router.go
func (r *router) handle(c *Context) {
n, params := r.getRoute(c.Method, c.Path)
if n != nil {
c.Params = params
key := c.Method + "-" + n.pattern
r.handlers[key](c)
} else {
c.String(http.StatusNotFound, "404 NOT FOUND: %s\n", c.Path)
}
}
router.go的变化比较小,比较重要的一点是,在调用匹配到的handler前,将解析出来的路由参数赋值给了c.Params。这样就能够在handler中,通过Context对象访问到具体的值了。
单元测试
func newTestRouter() *router {
r := newRouter()
r.addRoute("GET", "/", nil)
r.addRoute("GET", "/hello/:name", nil)
r.addRoute("GET", "/hello/b/c", nil)
r.addRoute("GET", "/hi/:name", nil)
r.addRoute("GET", "/assets/*filepath", nil)
return r
}
func TestParsePattern(t *testing.T) {
ok := reflect.DeepEqual(parsePattern("/p/:name"), []string{"p", ":name"})
ok = ok && reflect.DeepEqual(parsePattern("/p/*"), []string{"p", "*"})
ok = ok && reflect.DeepEqual(parsePattern("/p/*name/*"), []string{"p", "*name"})
if !ok {
t.Fatal("test parsePattern failed")
}
}
func TestGetRoute(t *testing.T) {
r := newTestRouter()
n, ps := r.getRoute("GET", "/hello/geektutu")
if n == nil {
t.Fatal("nil shouldn't be returned")
}
if n.pattern != "/hello/:name" {
t.Fatal("should match /hello/:name")
}
if ps["name"] != "geektutu" {
t.Fatal("name should be equal to 'geektutu'")
}
fmt.Printf("matched path: %s, params['name']: %s\n", n.pattern, ps["name"])
}
使用Demo
看看框架使用的样例吧。
day3-router/main.go
func main() {
r := gee.New()
r.GET("/", func(c *gee.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "<h1>Hello Gee</h1>")
})
r.GET("/hello", func(c *gee.Context) {
// expect /hello?name=geektutu
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello %s, you're at %s\n", c.Query("name"), c.Path)
})
r.GET("/hello/:name", func(c *gee.Context) {
// expect /hello/geektutu
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello %s, you're at %s\n", c.Param("name"), c.Path)
})
r.GET("/assets/*filepath", func(c *gee.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gee.H{"filepath": c.Param("filepath")})
})
r.Run(":9999")
}
使用curl工具,测试结果。
$ curl "http://localhost:9999/hello/geektutu"
hello geektutu, you're at /hello/geektutu
$ curl "http://localhost:9999/assets/css/geektutu.css"
{"filepath":"css/geektutu.css"}